 ADOxxWEB Simulation
ADOxxWEB Simulation
DETAILS: ADOxxWEB Simulation
The ADOxxWEB Simulation provides a fast and extendible service able to simulate business process executions. The service is provided through a REST interface that takes as input the model to simulate and some simulation parameters, and from that returns an XML file with simulation results. The service is focused on business process models but is flexible enough to be adapted to simulate any kind of models. The simulation service provides additionally an asynchronous HTML/JavaScript client in order to use and test the service without integrating it in a tool.
How it Works
The service internally uses a Petri Net structure in order to represent the model to simulate. The semantics of the simulation, in this way, relies on Petri Net strong formalism. In the case of Business Process models, the simulation uses state-of-the-art mapping rules in order to import the model as a Petri Net. This import phase can also be skipped, providing a Petri Net model in PNML standard format directly to the simulator. This gives the possibility to simulate any kind of model that can be expressed as a Petri Net, also generated by external systems.
The services expose REST APIs in order to be easily integrated in every system. Examples of such integration have been provided in ADOScript format for ADOxx and as an MFB template for Adonis NP.
The Simulation service also provides an asynchronous HTML/JavaScript client in order to use and test the service without integrating it in a tool.
Features and Functionality
The simulation service exposes the following characteristics:
- Automatic model identification:
The simulation service is able to automatically recognize the following XML formats in which a model can be provided: BPMN2 OMG, ADOxx Xml, Adonis Light Xml, and PNML. When BPMN2 is provided, the model is converted to a Petri Net using state-of-the-art mapping rules. In the cases of ADOxx and ADONIS NP, the same mapping rules are used. But, multiple petri nets can be generated in these cases; one for each Business Process model present inside the XML. Instead, when a PNML model is provided, it is loaded directly into the simulator as it represents a Petri Net.
- Wide range of Managed BPMN Concepts:
An extended set of mapping rules from BPMN to Petri Nets have been implemented. This rules concern all kinds of tasks and intermediate events, sub-process, start and end events (with and without messages), looping tasks, bounded events, exclusive gateways, parallel gateways, inclusive and complex gateways, event based gateways, sequence flows and messages flows. All of these concepts are supported from both BPMN OMG models and ADO Business Process models.
- Extensible Measures System:
The simulator implements an event based measurement system that gives the possibility to easily add simulation indexes through the definition of listeners. The currently supported indexes are Costs, Execution Times and Waiting Times (which are automatically calculated on the execution times). Additionally, the simulator implements the concepts of Traces and Paths through which the indexes are calculated.
- Extensible Transitions Probability Management System:
The base mechanisms automatically choose between parallel paths and paths with predefined probabilities of executions. Missing probabilities are automatically calculated. An extension of this system has already been provided, which adds support of dynamic probabilities through the use of JavaScript code.
- Light Results:
In the case of big or high looping models, the simulation results can be heavy to transfer over the network. In particular, the high number of traces and paths can affect system performance. For this reason, a light result feature has been implemented. In such a case, detailed results are avoided and only partials are provided.
- Integration with ADOxx and Adonis NP:
The simulation service has been successfully integrated in ADOxx through the definition of a specific mechanism in ADOScript, and in Adonis NP through the creation of a MFB Plug-in. Both act as clients for the simulation service. The service also provides an asynchronous HTML/JavaScript client in order to use and test the service without integrating it in a tool.
Architecture
In this section, the high level architecture of the simulation service is provided:
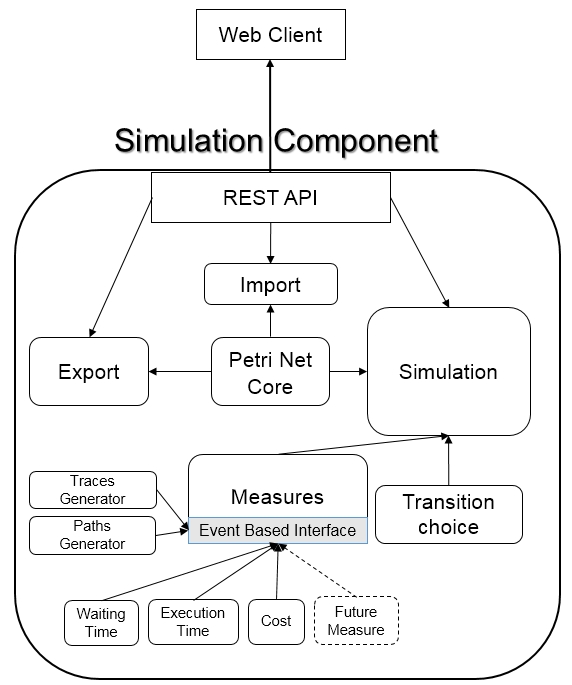
The Petri Net Core Module is the component that contains the main logic of a Petri Net and manages its semantics. The simulation service uses this component in order to evaluate which transition can be enabled at each step.
The Import Module is an easy to extend component that is able to automatically recognize the format of the provided model and converts it into the internal Petri Net structure. It manages separately the logic of document parsing, and of object mapping, in order to reuse the same mapping logic for multiple file formats (like in the case of BPMN and ADOxx BPMN).
The Export Module is for diagnostics only. It gives the possibility to export the internal Petri Net structure in the PNML standard format in order to be visualized in any supported editor.
The Simulation Measures Module is an easy to extend component that gives the possibility to define listeners for the simulation event. Each listener produces a measure or a result from a single simulation, like a trace, a path, the waiting times or the execution costs. The resulting indexes can then be collected in a special container in order to calculate some final indexes (like average values).
The Simulation Transition Choice Module is the component that performs the choice of the transition to execute between the available one. The module provides a base mechanism that performs a fear choice between parallel transitions and a user defined probabilistic choice between concurrent transitions. The base mechanism has also been extended in order to support dynamic probability evaluation using a scripting system.
The Simulation Module is the component that manages all the simulations, invoking the functionalities of the measures module and of the transition choice. It is also responsible for the generation of the simulation output in a structured XML format.
 www.adoxx.org
www.adoxx.org