 Developer Resources: Toolkit
Developer Resources: Toolkit
This Modelling Environment provides a collection of model types for business process oriented learning, individual training, business process support and reflection, process optimization and organizational evolution.
Download
Instalation Package:
LearnPAd Modelling Environment v4.0 Installation Package
Models:
TitoloUnicoModelSet.adl
EPBR-CoordicatorModelSet.adl
Model Type Overview
This tool contains a range of model types to effectively achieve these ends
- Business Motivation model
- Business Process model
- Case Management model
- Organizational model
- Competence model
- Documents and Knowledge model
- KPI model
- BPCMN model (tbd)
- Sentry model (tbd)
- RAMN Overview Model (tbd)
- RAMN Risk-Centered Model (tbd)
- Risk Library (tbd)
- Decision Model (tbd)
- Data Model (tbd)
- Planning Elements (tbd)
- Control Elements (tbd)
- Decision Requirements (DMN) (tbd)
- Decision Model (TDM) (tbd)
Below one can gain an overview of each of these model types.
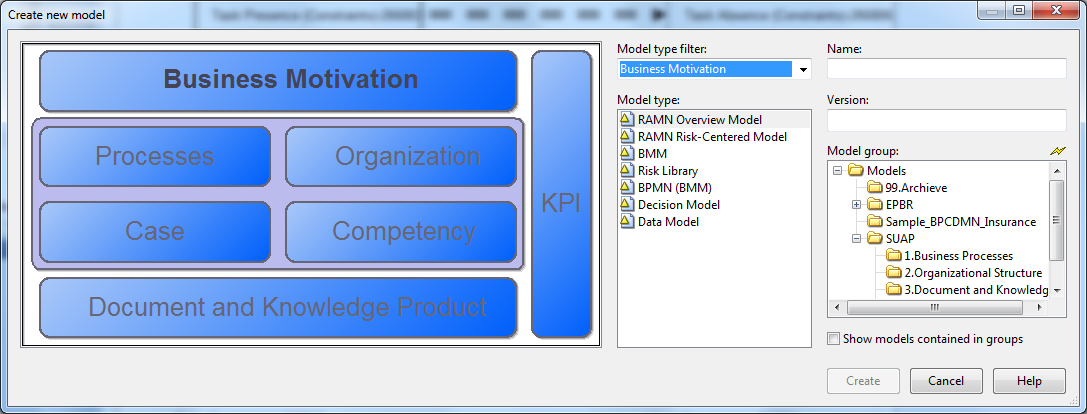
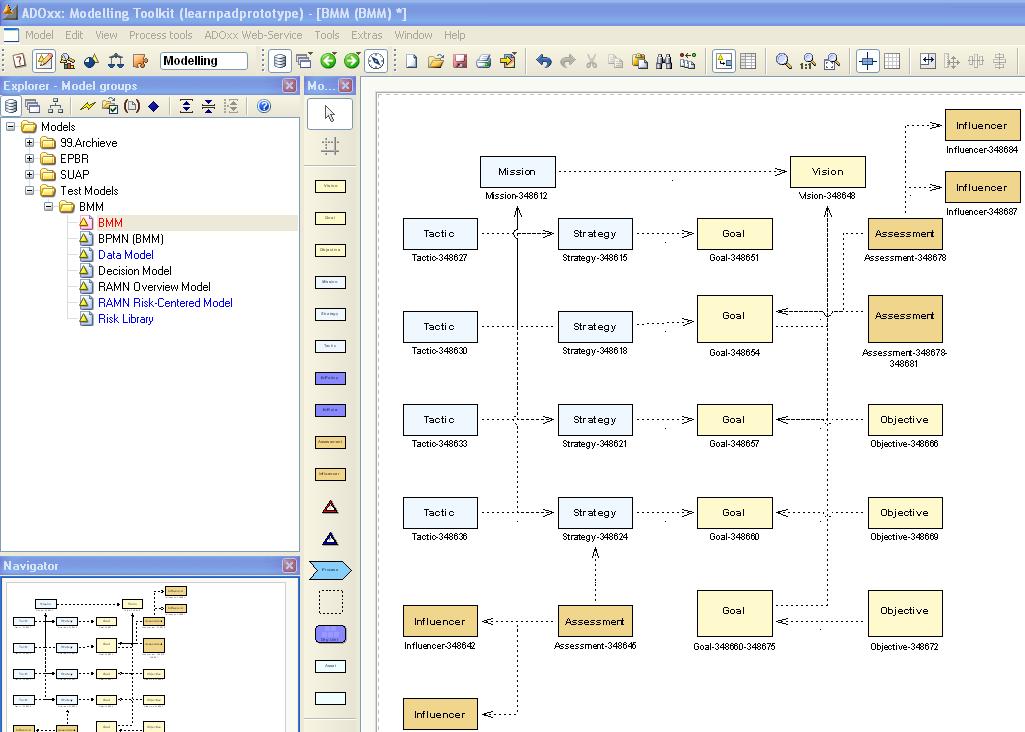
Business Motivation Model
Fundamental to the Business Motivation Model (BMM) is the notion of "motivation". If an enterprise prescribes a certain approach for its business activity, it ought to be able to say "why"; that is, what result(s) the approach is meant to achieve. Sometimes it is difficult to uncover such motivation, especially in operations that have been going on for some time.
For cases in public administration, this BMM tool allows one to encapsulate in the modelling environment, precisely what the vision and goals are, the discrete and progressive steps of how they may be attained and crucially, how to assess whether they have been achieved or not.
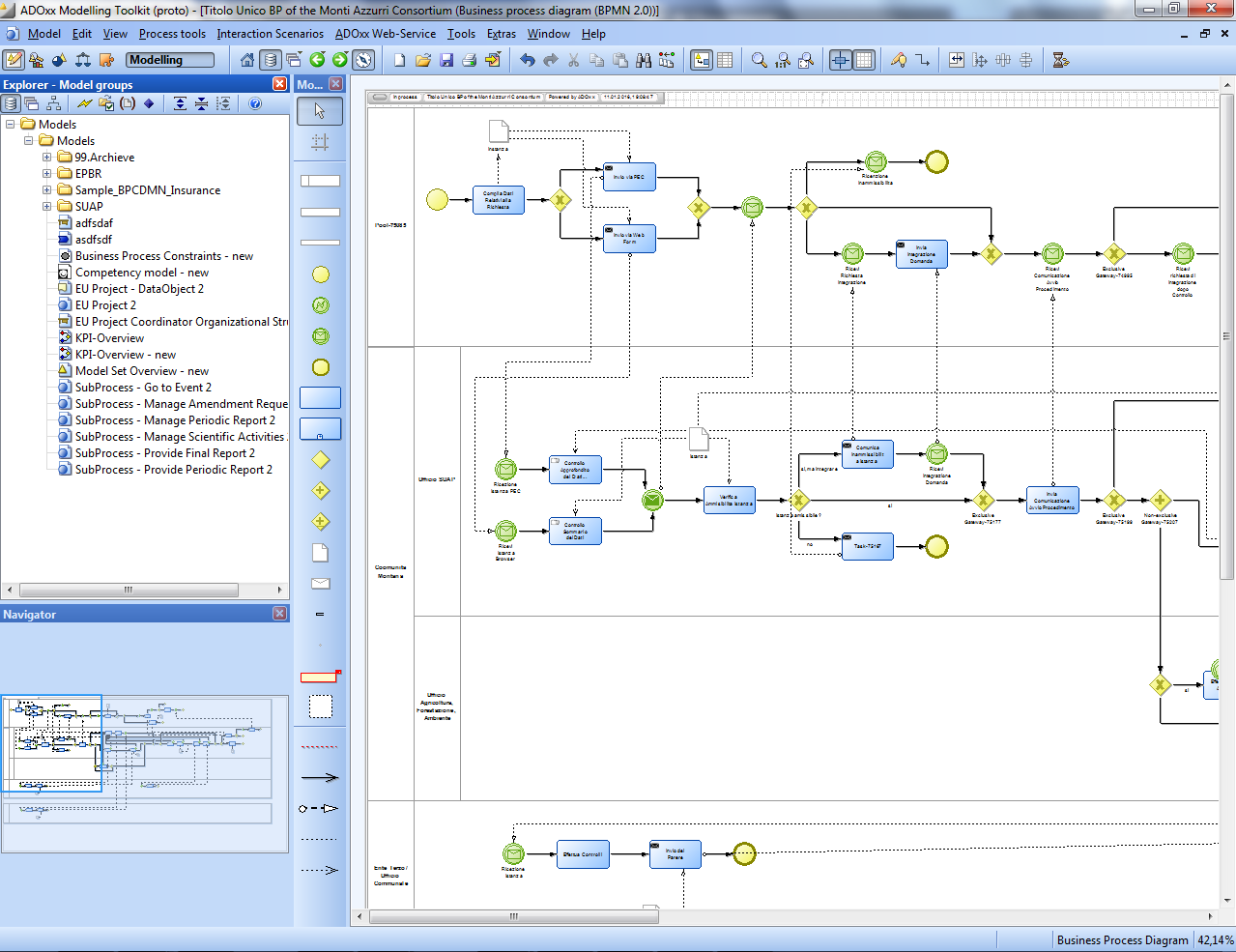
Business Process Model
This metamodel defines a minimal subset of BPMN 2.0 that Learn PAd intends to use for describing business processes in public administration domain for learning purpose. The subset is selected based on practical experience of Learn PAd partners working with Public administrations and the Learn PAd requirements.
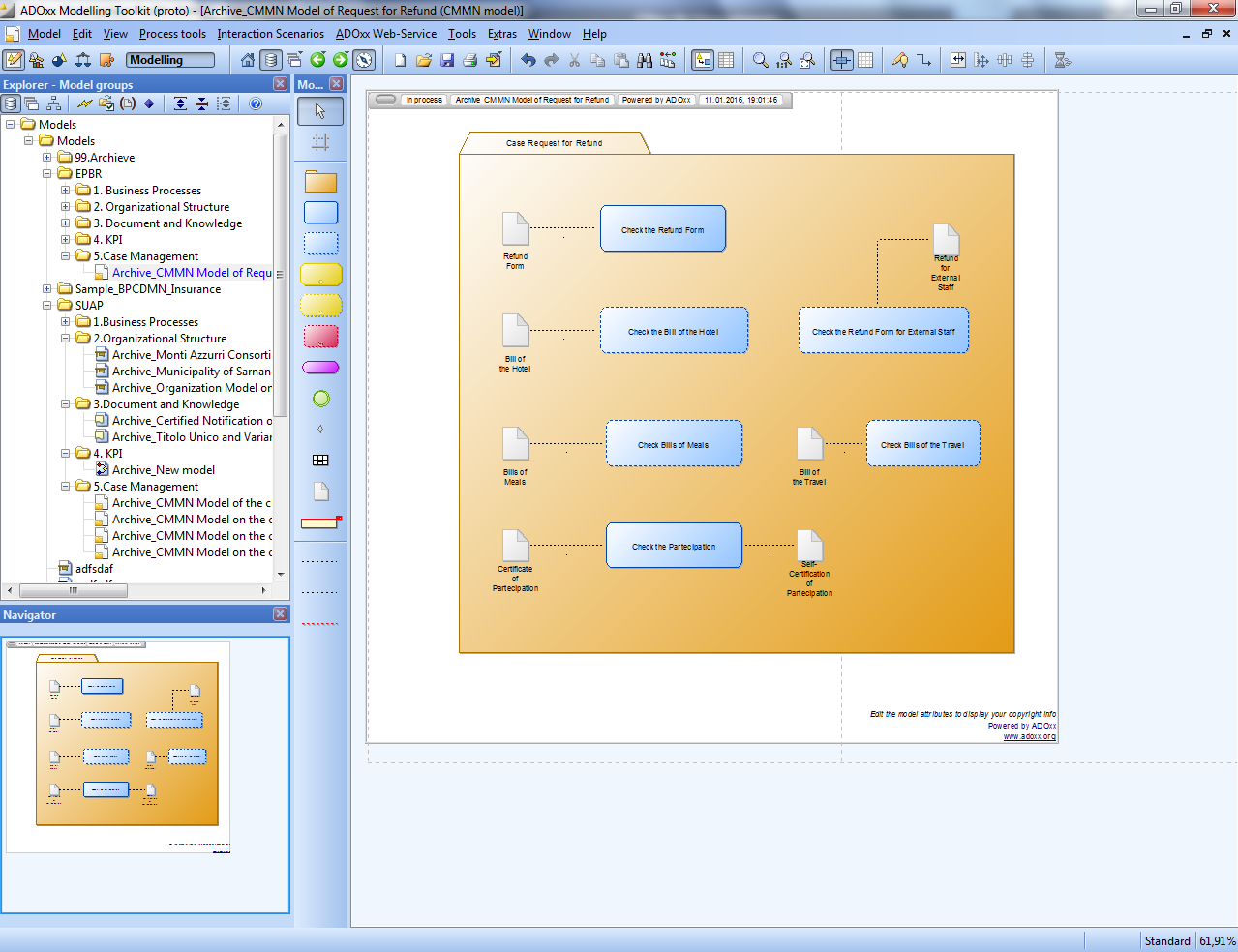
Case Management Model
Case management requires modeling and notation which can express the essential flexibility that human case workers, especially knowledge workers, require for run-time planning for the selection of tasks for a case, run-time ordering of the sequence in which the tasks are executed, and ad-hoc collaboration with other knowledge workers on the tasks. The CMMN specification defines a common meta-model and notation for modeling and graphically expressing a case. The specification is intended to capture the common elements, while also taking into account current research contributions on case management. Because BPMN does not deal with knowledge intensive tasks, CMMN is used for modelling knowledge-intensive (sub)-processes in Learn PAd.
For LearnPAd purposes the CMMN metamodel has been adapted and reduced in complexity through the addition of three additional concepts (PlanElement, Rule and CaseActivity).
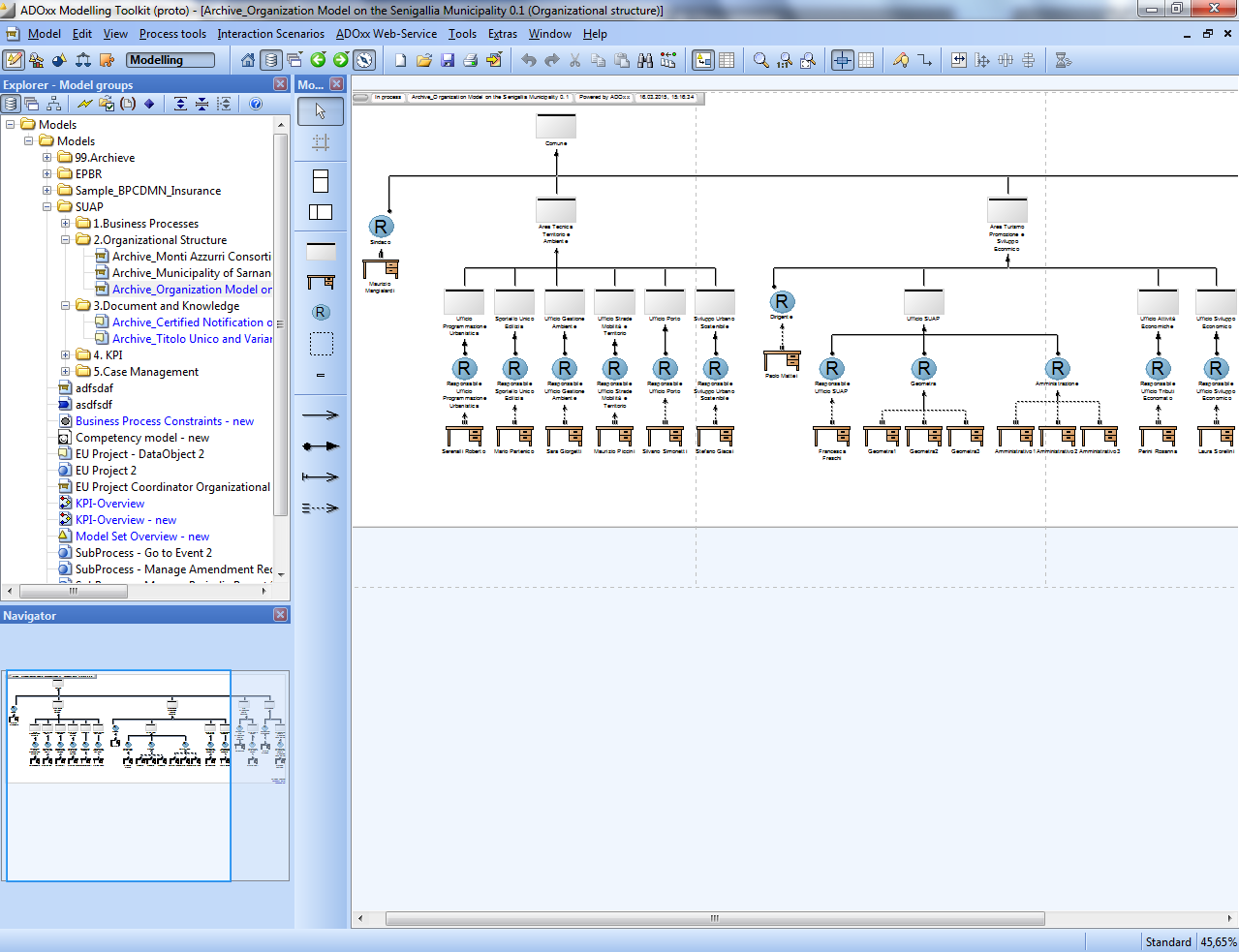
Organization Model
Organization models describe the structure of an organization (organization chart). In LearnPDa rganizational structure models can be built hierarchically using organizational sub models to e.g. illustrate a detailed structure of a working environment.
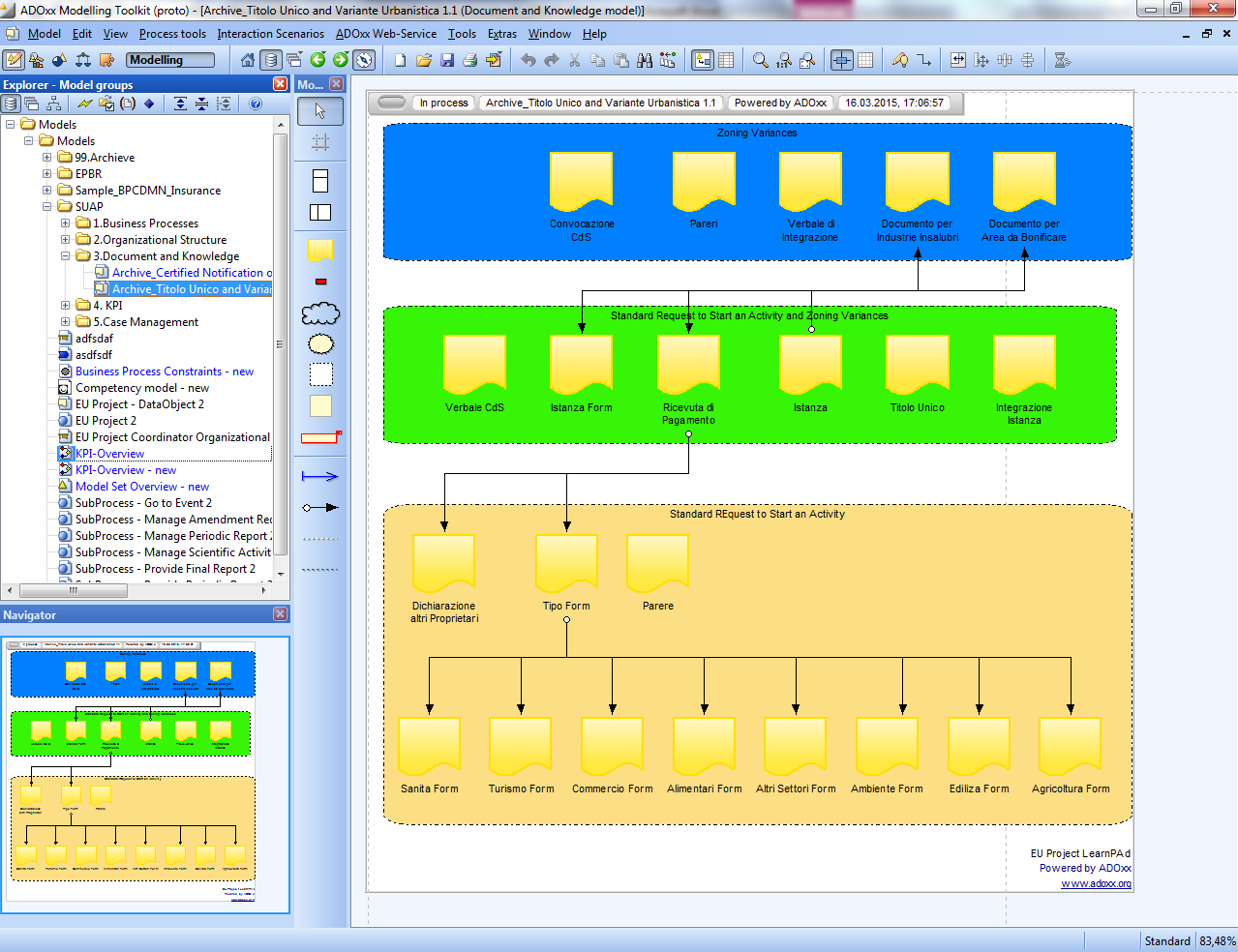
Documents and Knowledge Model
Knowledge models contain documents (templates), knowledge products knowledge resources, which are utilized in the processes (input, output to activities etc.). Knowledge models can be built hierarchically using document sub models to e.g. illustrate a detailed structure of documents.
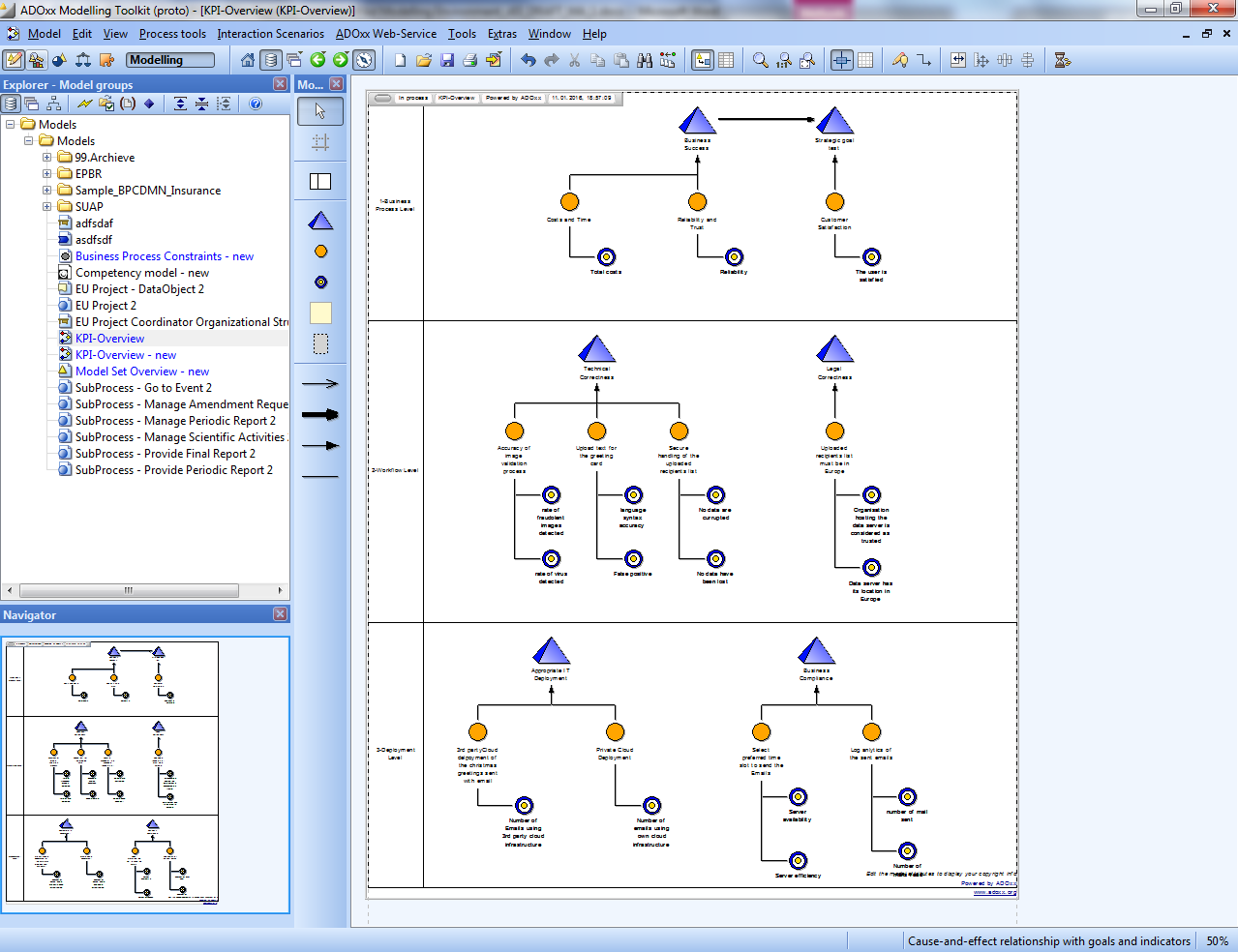
KPI Models
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are seen as a virtualisation instrument enabling to conceptualise relevant parts of the concrete instances of the production processes. A performance indicator is a measurement of the success of a given organization or activity in which it engages. Thus, KPIs can be succesfully employed in process models in order to assess performance of activities and processes.
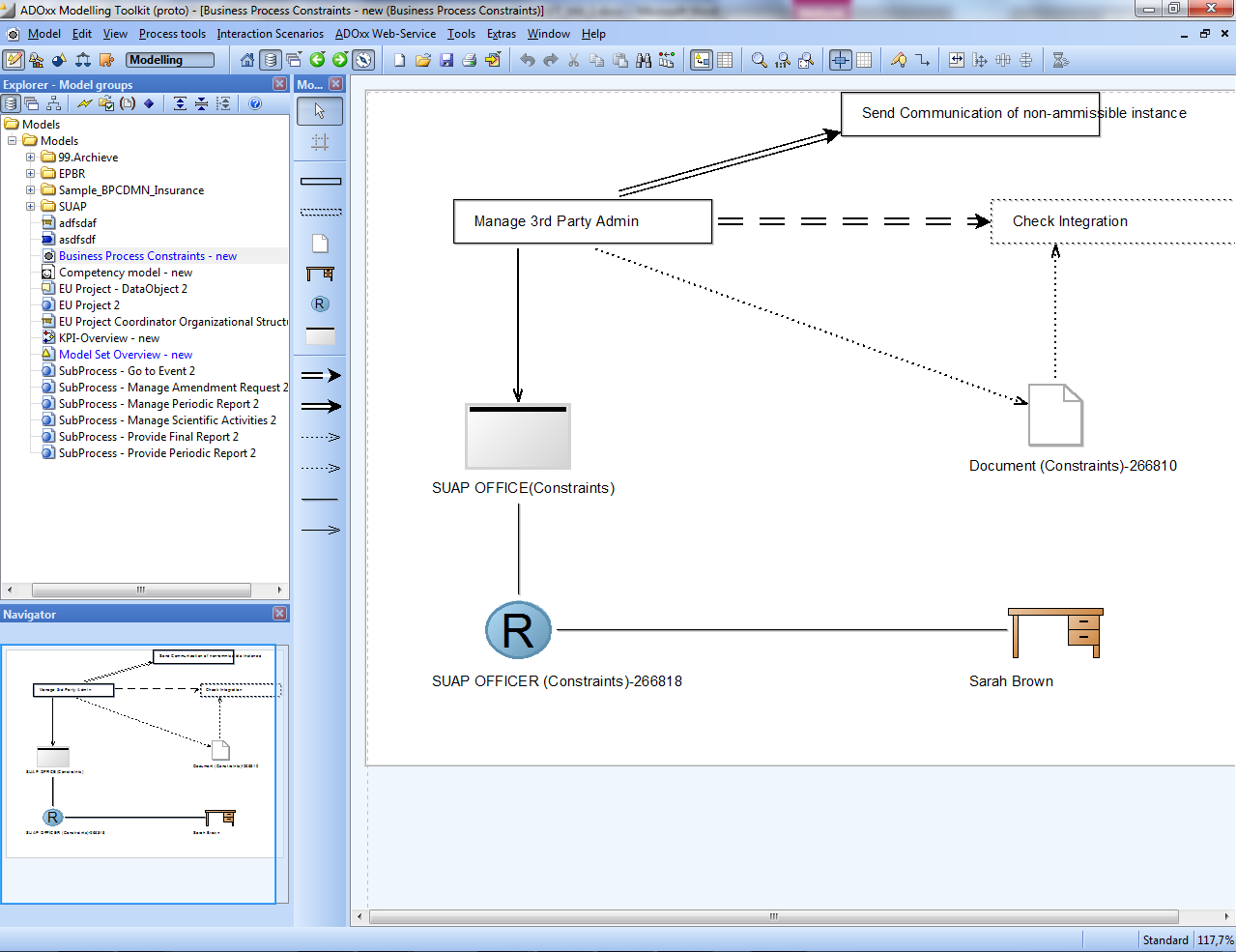
Business Process Constraint Model
The Business Process Constraint Model give the possibility to perform compliance checking as specified in deliverable 4.1 using the extended Compliance Rule Graphs (eCRG) formalism. The compliance properties defined involve the control flow, the data flow and resource perspectives. It actually consists of compliance rules, which may: impose constraints on the control flow schema of process models, constrain the data to be managed, require certain types of activities to be present in a process model, or enforce access control policies.
About the control flow is it possible to define temporal constraints on task subsequence. In particular is it possible to model the occurrence (or not) of a task eventually or definitely followed by the occurrence (or not) of another task in the future.
Constraints about data are specified using the Document (Constraints) object. This object can be related with a Task object in order to constraint the association of the document to the task.
The Role, Organizational Unit and User constraints in the end give the possibility to create compliance rules on the organizational model and on access control policies. In particular is possible to relate this three objects together in order to define rules, while is it possible to relate one of this objects to a task in order to define access and execution policies.
Competency Model
The Competency Model Type is realized in Learn PAd based on recommendations of the European Committee for standardisation, CEN WS-LT LTSO[1], driven by 9 international institutions and organizations involved in the standardization of E-learning technologies. (Refer to D3.2 for a class diagram of the Competency Model of the LPIMM; and to D5.1 for details on the ontological representation).
Furthermore the ECF (European Qualifications Framework) is taken to determine the object type 'competency', comprising descriptions of competence, skills and knowledge along with their levels. With this competencies modelled in Learn PAd become understandable and comparable. Marche Region initiated the competency model based on EQF, which has then been cooperatively enriched by FHNW and Marche Region.
The competency model contains all competencies required by an organization to reach its goals, be it on strategic or operational level, be it on organization or team level, be it by a role or for specific tasks.
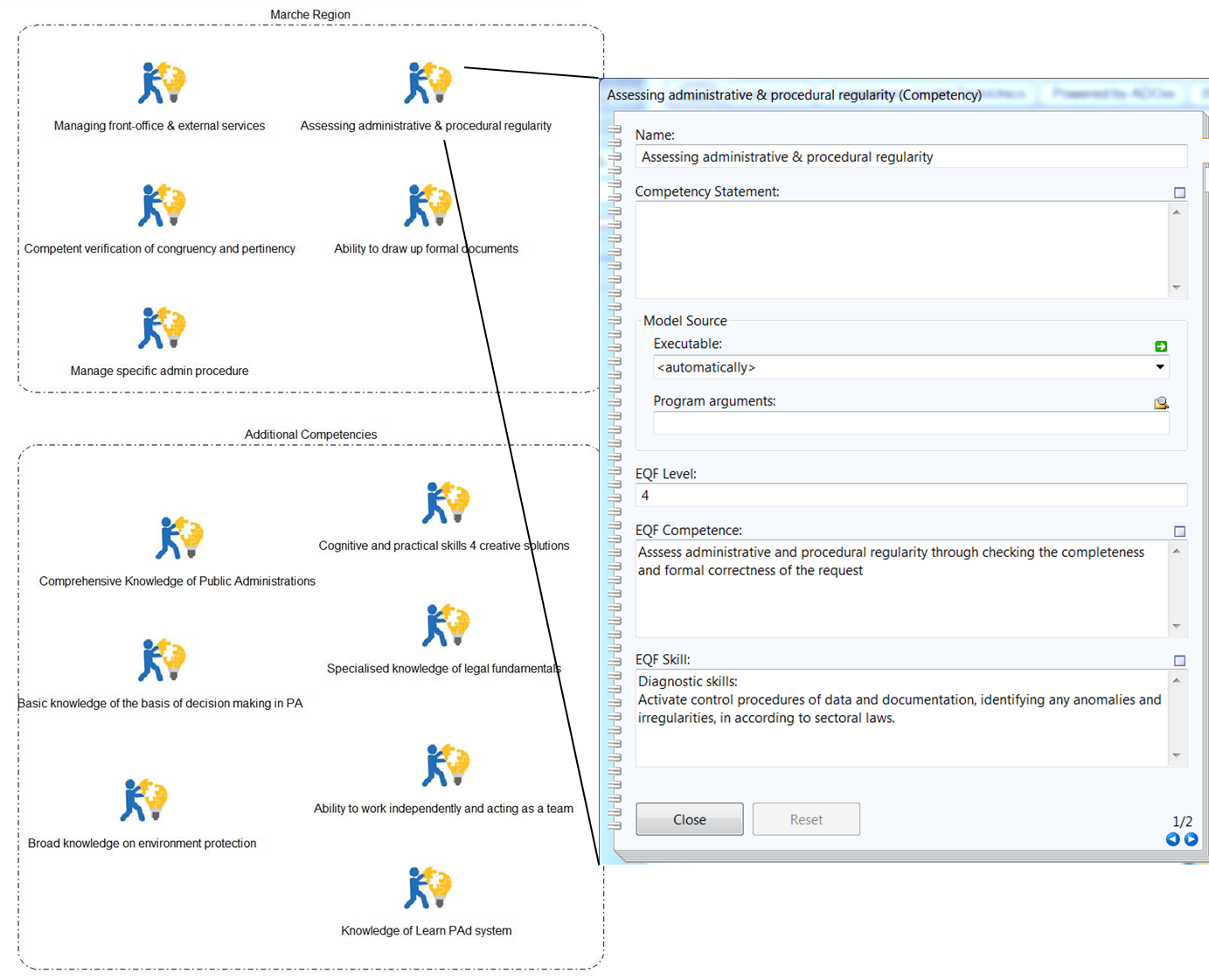
To determine what competencies are required for what, respectively on what level, competency profiles are created. Competency profile is a specific type of document (defined in the document and knowledge meta model) to group competencies that are required - for example needed to fill a role or meet objectives of an organizational unit - and acquired by individuals, i.e. by PA staff.
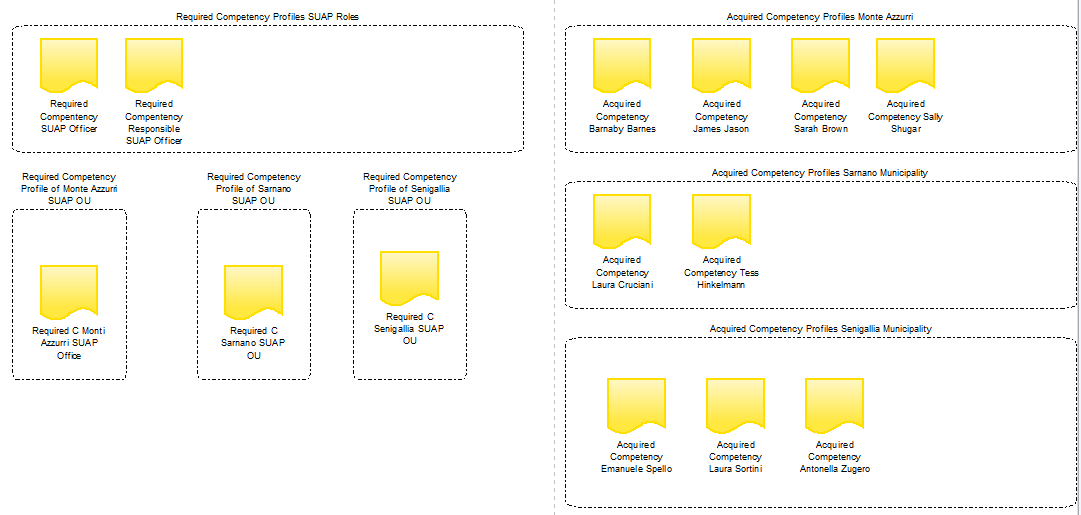
Assume, a new employee is assigned the role SUAP officer then the required competencies of this employee are the ones determined by the role (and eventually additional ones determined by the organizational unit she belongs to or specific tasks she has to perform). However, the acquired competencies this employee has when she starts the job might not be totally equal to the required ones or might be on a lower EQF level. The difference between the acquired and required competencies determines the individual learning goal.
Model Set Overview Model
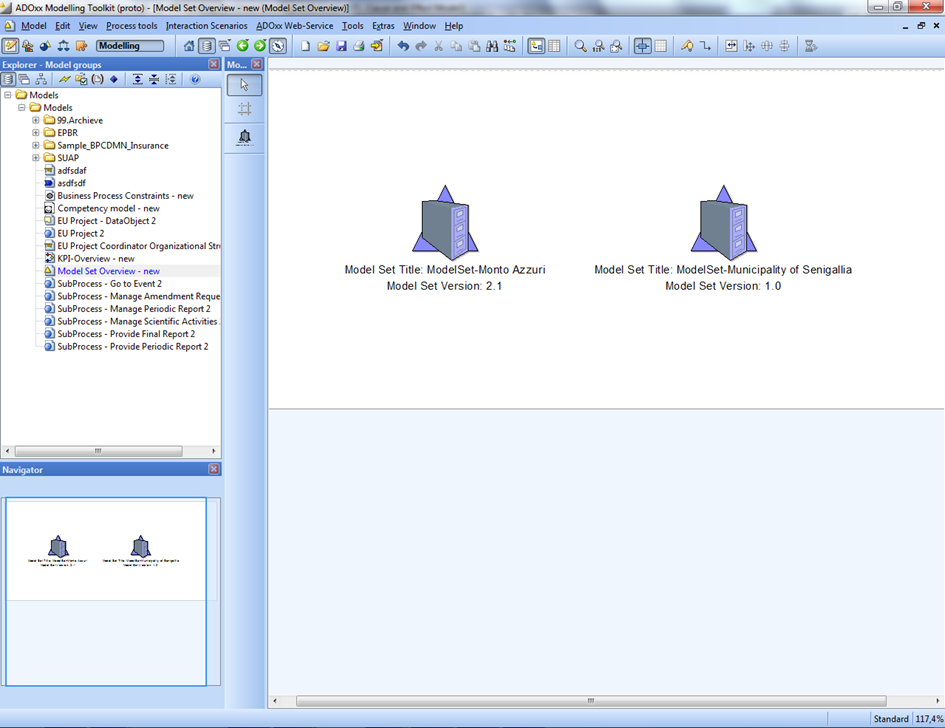
This model type is utilized to define scenario specific model sets to be pushed into the Learn PAd Core Platform and to be transformed. In this model type we have only one concept called "model set", which persists the information of model set id, version, short description about model set and every pointers individual model relevant for given scenario. Antoher goal of this model type is enabling to reuse models in different scenarios and give the possibility to define/check required models for given scenario. Besides those, this model type allows to persists model set specific feedbacks and patches retrieved from Collaboration Workspace through the LearnPAd Core Platform.
Modelling Features
There are a number of features available to facilitate modelling
- Semantic Lifting
- People-Like View
- Bar Display View
- Comments Sidebar
Interactive Scenarios between LearnPAd Modelling Environment and LearnPAd Core Platform
- Push New Model Set into Core Platform and Start Verification and retrieve Results
- Retrieve Feedbacks about Model Artefacts from Wiki
Semantic Lifting
Semantic lifting allows integrating human-interpretable models with the machine interpretable Ontology built in WP5, which required by the Learn PAd Recommender system. Semantic Lifting Mechanism is a generic mechanism, which means it can work on each meta-model, hence can be applied on every model type.
Semantic lifting is a form of a loose coupled model weaving, where concepts of a business process – e.g. tasks – are semantically lifted. This semantic lift is implemented by annotating the concept with an ontological concept. Hence, each object in a business process model can optionally be annotated with an ontology concept.

Push New Model Set into Core Platform and Start Verification and retrieve Results
Using the Model Set Overview Model Type it is possible to push a Model Set to the LearnPAd Platform. All the models in the model set are first exported as XML, images, image maps and (only for business process model type) as BPMN2.0 and subsequently are zipped and sent to the LearnPAd Platform. An unique ID for each model set, is automatically generated and is used to reference the model set inside the platform and be retrieved by other components like the Verification Component.
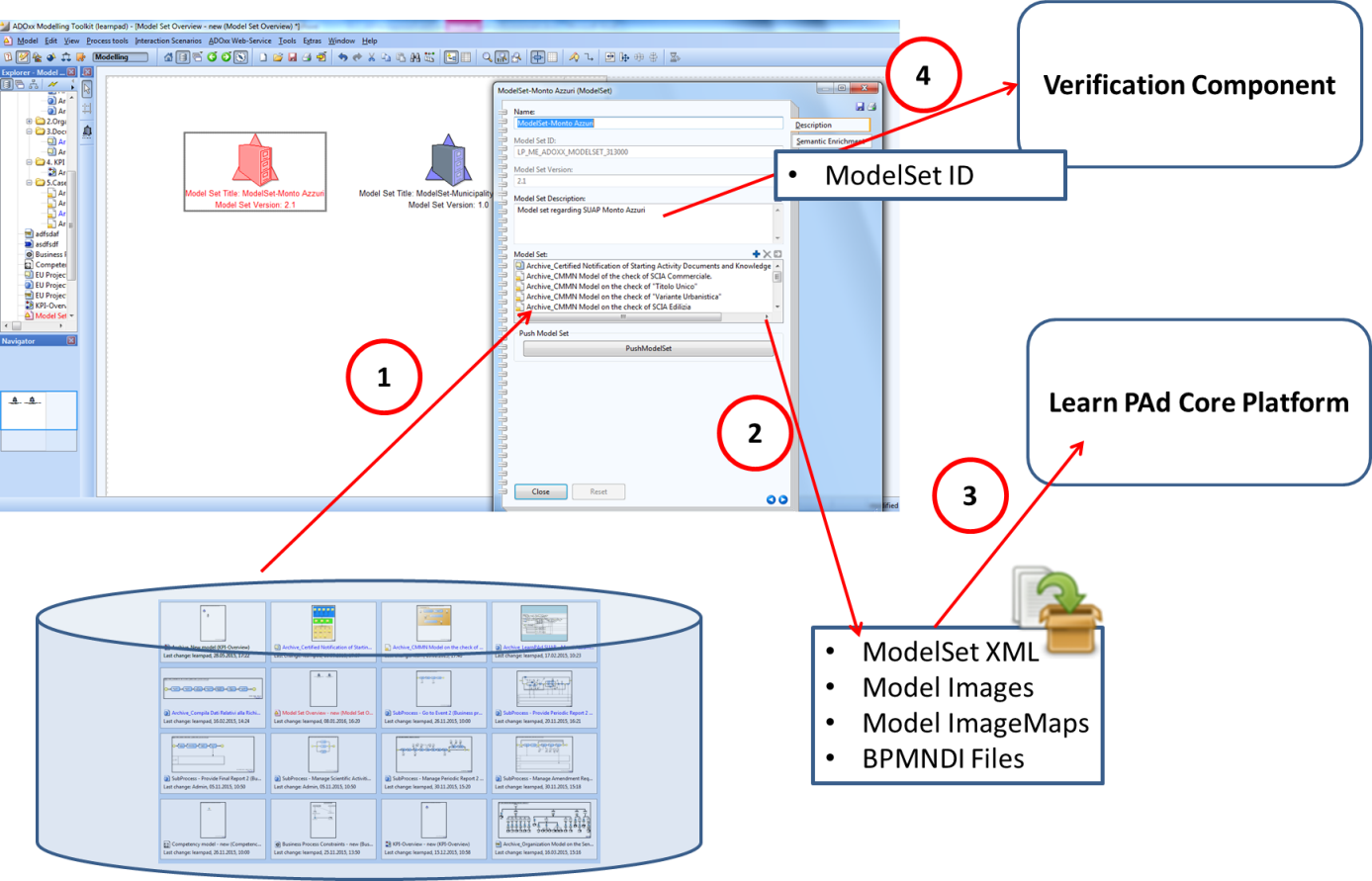
The Modelling Environment can then start a model set verification of a previously pushed model set. The list of all available verification type provided by the LearnPAd Platform is displayed to the modeller, and once the verification is started, a unique verification Id is associated to the model set. This verification Id will be used to retrieve the verification results once completed.
The results will be showed directly in the Modelling Environment in a user friendly way.
Retrieve Feedback and Patches from XWiki
A user of the LearnPAd platform can release feedback and apply patches on a model or a specific object of a model in order to improve it or report a mistake. The modeller can retrieve this feedbacks from the Modelling Environment and take care or reject them.
Every feedback is in the form of a comment box associated to the relative object involved.
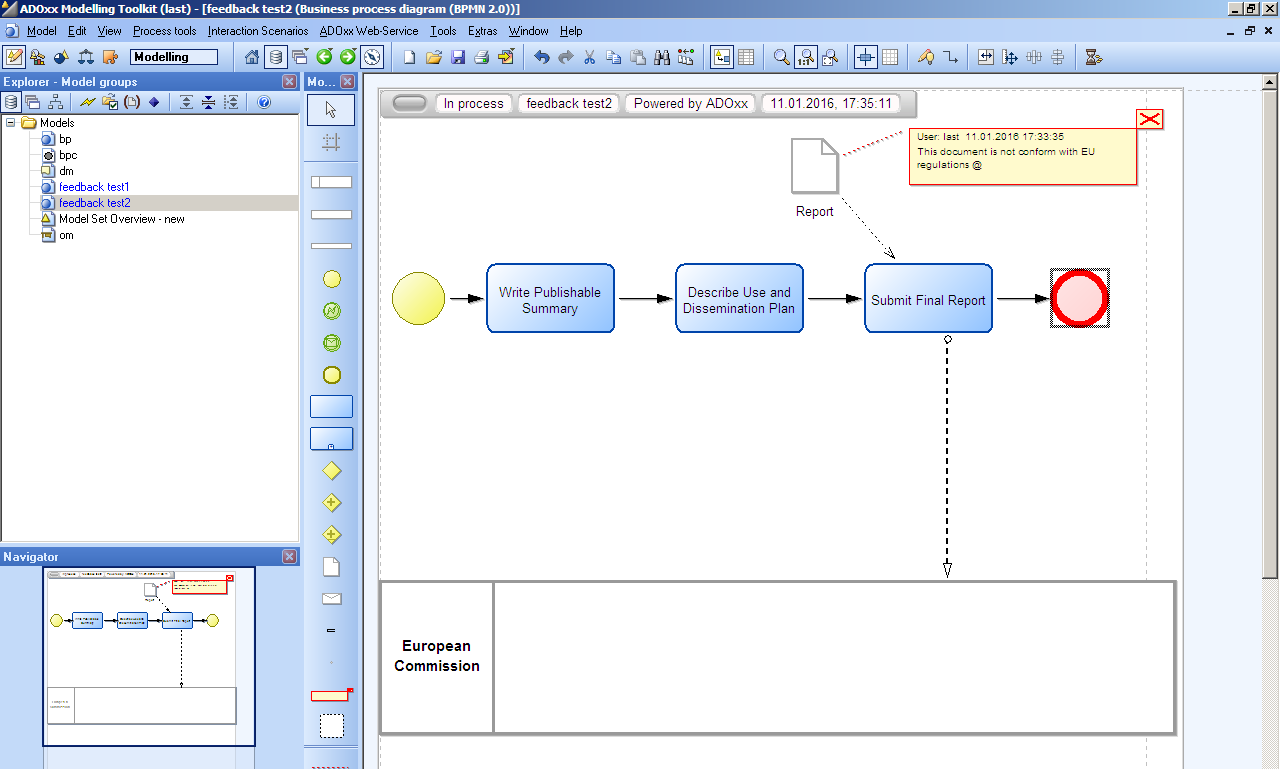
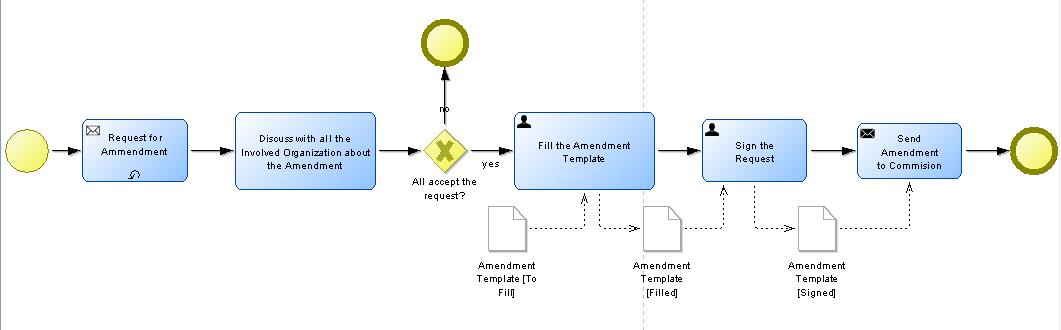
People-Like View
In order to ease the interpretation of business processes, so-called people oriented view has been introduced that enables the switch form a business process in traditional graphical notation to a new graphical notation, where icons graphically describe the nature of the activity.
This is achieved, by a semantic lifting of each concept, hence the relation of a model object with an ontological description. A list of explanatory graphical icons is also annotated to the same ontological description. Hence, when switching into the people-like view, the images that are annotated with the model object are included in the new graphical description.
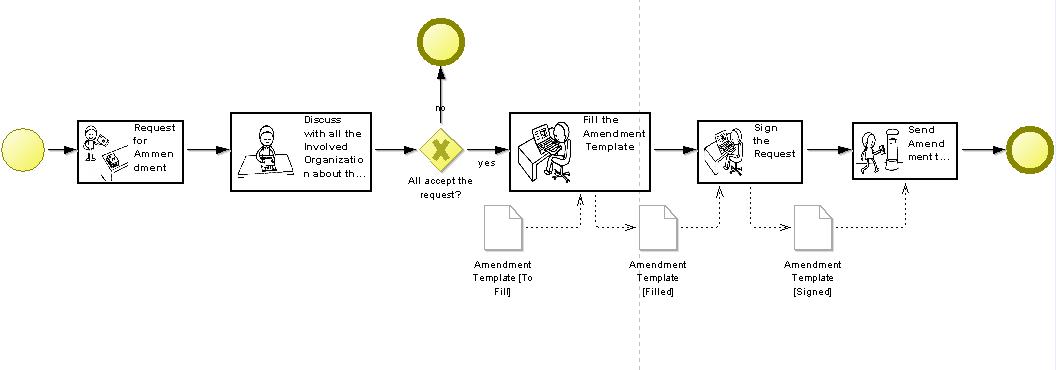
Bar Display View
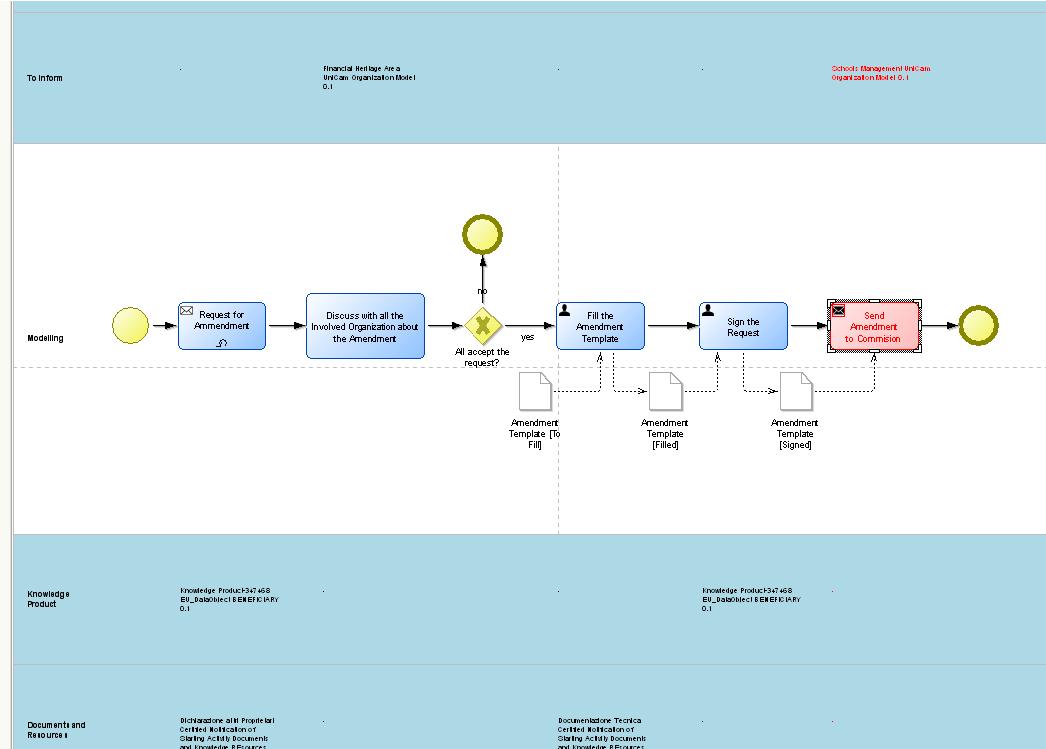
Zoomed in, we can see the object properties with intermodel references and links to related objects which can be clicked on to display the associated model or object.
The available area for modelling and the size and display of individual bars can be user controlled and the display view can be set as vertical or horizontal.
For a detailed documentation of this functionality, please refer to:
Comments Sidebar
The Comments Sidebar can be used for on the fly commenting of certain object instances, facililitating more efficient model development and collaborative work. On activation of the Commenting Sidebar, the drawing area is divided into an area where modelling is performed and an area where comments for each object are displayed; the bar itself can be placed horizontally or vertically
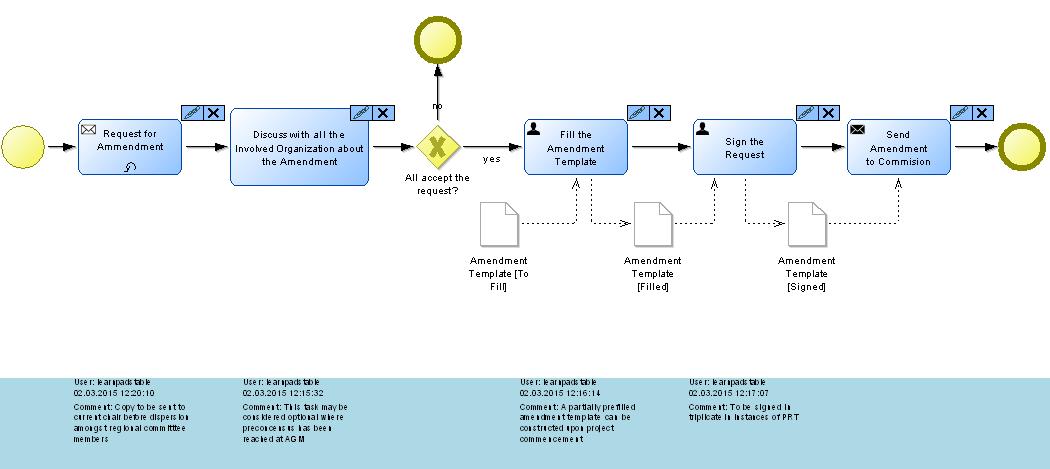
Each commentable object then receives two tabs at the top-right corner, one to comment the object and one to delete a comment associated with the object
Upon entry of a comment, the comment itself is displayed in the comment bar directly across from or below depending on the orientation of the comment bar. The comment also displays the user that made the comment and the time and date when the comment was made
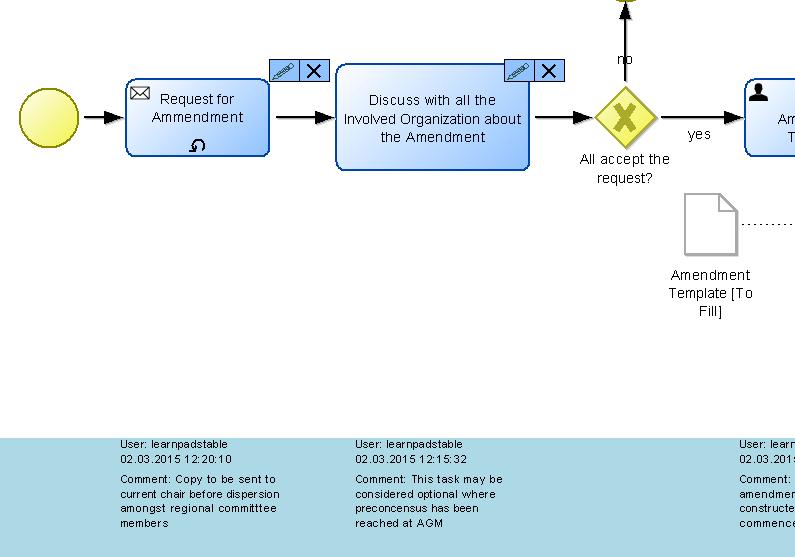
Model sets:
Here we describe the contents produced in order to finalise the Learn PAd platform and plan the final evaluation. To produce them we use the version 4.0 of the Learn PAd Modelling Environment. Such contents referring both the cases studies: SUAP and EPBR. You can download the two model sets above in the download section.
SUAP refers to activities that the Italian Public Administrations have to put in place in order to permit entrepreneurs to set up new companies or generally to organize business activities. Reducing the administrative burden the entrepreneurs refer to a single office, the SUAP office. Contact between entrepreneurs and SUAP office has to be done completely online. SUAP office can be considered as a mediator among entrepreneurs and PAs. It means that in case an entrepreneur wants to start a manufacturing activity, he/she needs just to contact the SUAP office that is in charge of forwarding the request to all the other involved administrations. In order to produce the final version of the content we focused on Titolo Unico BP since it result to be the procedure impacting more on the workload of civil servants.
EPBR refers to activities that the Italian Public Administrations have to put in place in order to report about activities done in the context of EU project. The grant management BP has been selected as reference point for the European Project Budget Report. Grant management includes some sub-process, they are: Periodic Report, Final Report, Manage Payment and eventually Manage Amendment. Considering intra-organizational perspective, we focus on the the case of an Italian public research body acting as Coordinator since it is the most complete scenario.
For both the cases the models we include are following listed:
· Business Process model;
· Organizational model;
· Documents and Knowledge model;
· Competence model;
· Business Motivation model.
The KPI model is also included in a very preliminary version since the work on KPI in ongoing and the Deliverable D5.4: KPI Ontology and Learners Assessment Mechanisms is due on M27. Finally, Case Management model is not included since the knowledge intensive scenarios has been described trough BPMN 2.0.
 www.adoxx.org
www.adoxx.org